Content
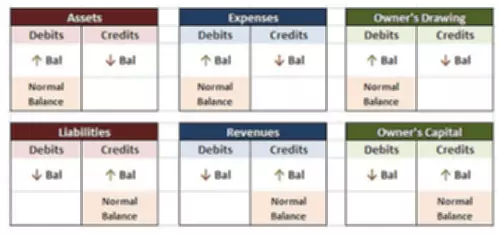
Retained earnings appear under the shareholder’s equity section on the liability side of the balance sheet. Retained earnings are the residual net profits after distributing dividends to the stockholders. You may also distribute retained earnings to owners or shareholders of the company.
This balance is generated using a combination of financial statements, which we’ll review later. Most businesses include retained earnings as an entry on their balance sheet. The figure appears alongside other forms of equity, like the owner’s capital. However, it differs from this conceptually because it’s considered to be earned rather than invested.
Retained Earnings: Formula & Calculation
For an analyst, the absolute figure of retained earnings during a particular quarter or year may not provide any meaningful insight. Observing it over a period of time (for example, over five years) only indicates the trend of how much money a company is adding to retained earnings. If you’ve prepared this statement before, you’ll carry over the last period’s beginning balance. If this is your first statement of retained earnings, your starting balance is zero. Remember that retained earnings equals equity, and so should not appear anywhere in the assets and liabilities parts of the balance sheet.
- However, retained earnings is not a pool of money that’s sitting in an account.
- This might include hiring new people, implementing new marketing campaigns or doing research and development on a new product or location.
- Editorial content from The Ascent is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.
- As we mentioned above, retained earnings represent the total profit to date minus any dividends paid.
- Since all profits and losses flow through retained earnings, any change in the income statement item would impact the net profit/net loss part of the retained earnings formula.
Business revenue is calculated period by period and recorded at the top of your income statement. Retained earnings on a balance sheet usually refer to the accumulated earnings. When retained earnings are cumulative, it means that the current year’s retained earnings are added to the previous year’s retained earnings. how to calculate retained earnings This cumulative total is the sum of all retained earnings since the company was founded. In other words, cumulative retained earnings represent the total amount of all past retained earnings from previous years. This number can provide an idea of how much money has been reinvested back into the business over time.
Startups often have negative retained earnings.
It is a measure of all profits that a business has earned since its inception. Therefore, it can be viewed as the “left over” income held back from shareholders. Retained earnings reflect the amount of net income a business has left over after dividends have been paid to shareholders. Anything that affects net income, such as operating expenses, depreciation, and cost of goods sold, will affect the statement of retained earnings. As with all aspects of accounting, accuracy is important when calculating a retained earnings statement—and as startups grow, those calculations can become more complex.
After adding the current period net profit to or subtracting net loss from the beginning period retained earnings, subtract cash and stock dividends paid by the company during the year. In this case, Company A paid out dividends worth $10,000, so we’ll subtract this amount from the total of Beginning Period Retained Earnings and Net Profit. By subtracting the cash and stock dividends from the net income, the formula calculates the profits a company has retained at the end of the period. If the result is positive, it means the company has added to its retained earnings balance, while a negative result indicates a reduction in retained earnings. Remember that your company’s retained earnings account will decrease by the amount of dividends paid out for the given accounting period. When calculating retained earnings, you’ll need to incorporate all forms of dividends; you’ll see that stock and cash dividends can impact the final number significantly.
Are retained earnings a type of equity?
Now, if you paid out dividends, subtract them and total the Statement of Retained Earnings. You will be left with the amount of retained earnings that you post to the retained earnings account on your new 2018 balance sheet. On one hand, high retained earnings could indicate financial strength since it demonstrates a track record of profitability in previous years. On the other hand, it could be indicative of a company that should consider paying more dividends to its shareholders. This, of course, depends on whether the company has been pursuing profitable growth opportunities.
This represents capital that the company has made in income during its history and chose to hold onto rather than paying out dividends. One way to assess how successful a company is in using retained money is to look at a key factor called retained earnings to market value. It is calculated over a period of time (usually a couple of years) and assesses the change in stock price against the net earnings retained by the company. In this article, we’ll provide the retained earnings formula and explain how to prepare a statement of retained earnings.
How to Calculate Retained Earnings (Formula and Examples)
Retained earnings don’t appear on the income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement. The income statement will list a net income figure, which might seem to be the same as retained earnings but isn’t. The net income contributes to retained earnings but, as mentioned, retained earnings are cumulative across accounting periods, subject to dividends being taken out, and accounted for as an asset. Retained earnings can be used to pay additional dividends, finance business growth, invest in a new product line, or even pay back a loan. Most companies with a healthy retained earnings balance will try to strike the right combination of making shareholders happy while also financing business growth.
Both retained earnings and reserves are essential measures of a company’s financial health. Retained earnings are the profits a company has earned and retained over time, while reserves are funds set aside for specific purposes, like contingencies or dividends. In addition to providing the company with capital for growth, retained earnings also help improve its financial ratios, such as its return on equity.
Subscribe to the Sage Advice Small Business Newsletter
Since company A made a net profit of $30,000, therefore, we will add $30,000 to $100,000. The retained earnings amount can also be used for share repurchase to improve the value of your company stock. Thankfully, working out how to calculate retained earnings is simple and requires no complex mathematics. Any earnings retained after the business has met its obligations may be used to reward shareholders or focus on expansion. Below is a short video explanation to help you understand the importance of retained earnings from an accounting perspective. But while the first scenario is a cause for concern, a negative balance could also result from an aggressive dividend payout – e.g. dividend recapitalization in LBOs.